- by foxnews
- 08 Apr 2025
Leaked Doherty Covid modelling shows just the most worrying scenario ? not the most likely | Melissa Davey
Leaked Doherty Covid modelling shows just the most worrying scenario - not the most likely | Melissa Davey
- by theguardian
- 22 Dec 2021
- in news
Much of the pandemic modelling to make news headlines since Covid-19 hit has depicted concerning scenarios involving high case numbers and hospitalisations.
On Thursday, modelling from the University of NSW and cited by NSW health minister Brad Hazzard found Covid-19 cases in the state could reach 25,000 a day by the end of January. The latest modelling to raise alarm bells came from the Doherty Institute and was leaked to the media on Tuesday after being sent to politicians ahead of a meeting of national cabinet on Wednesday. It said Australia could see 200,000 new Covid cases a day by late January or early February.
Early into the pandemic in 2020, other models predicted "hundreds of thousands" of Australian deaths, while health workers in NSW were told to prepare for 8,000 deaths in the first-wave.
But these are worst-case scenario models and are just one scenario out of dozens of different scenarios that are calculated by epidemiologists and biostatisticians.
What is often lost in the reporting of these worst-case models is that they rarely ever eventuate, but are calculated to allow governments to see what might happen if they did nothing at all to control an outbreak, and to plan accordingly.
The leaked Doherty Institute modelling projecting 200,000 cases came with an important caveat; this would only eventuate if nothing was done, including if people did not change their behaviour at all of their own accords. It also assumed no change to the pace of booster roll-outs, and that only very basic restrictions such as requiring masks in hospitals are maintained.
But already, people are changing their behaviour in states like NSW where mask mandates for retail don't exist, wearing masks anyway to shopping centres, or cancelling bookings for crowded venues. The Australian Technical Advisory Group on Immunisation [Atagi] is constantly reviewing data on boosters, and adjusting its recommendations accordingly.
What doesn't make headlines are the other less worrying scenarios depicted by the Doherty Institute and other institutions that project what may happen if, for example, masks are worn, vaccines prove to offer fair protection against variants, or data changes on the reproduction rate of the virus. There is no one model or scenario experts rely upon, and models are constantly tweaked as more information is gathered about the virus.
Ahead of national cabinet meeting on Wednesday the chair of the Australian Health Protection Principal Committee, Prof. Paul Kelly, said of the 200,000 figure "presents one of the worst case of all potential scenarios including assumptions that the Omicron variant is as severe as the Delta variant, an absence of hospital surge capacity, a highly limited booster program, no change to baseline public health and social measures and an absence of spontaneous behaviour change in the face of rising case numbers".
"None of these five assumptions represent the likely state of events, let alone all of them together, therefore presenting that scenario as the likely scenario that will occur is highly misleading."
The problem is that when parts of reports leak ahead of time, the most concerning picture, rather than the full story, is often presented.
Chair of biostatistics and epidemiology at the University of South Australia, Prof. Adrian Esterman, said epidemiologists now model by creating individuals with certain ages, occupations, social movements, and other characteristics. It's known as agent-based modelling, and it is used by the Doherty Institute.
"They then do this a million times, each person with slightly different characteristics, then they simulate what happens when all of these individuals interact," Esterman said. "To do that, they not only have to enter all these details about each individual person, they have to add in the things like the generation interval of the virus, its incubation period, its effective reproduction number as well.
"And the point is, every single one of those things is an estimate, and is subject to change. So we now have dozens and dozens of parameters in the model, each of which are estimates creating 'what if' scenarios.
"Taken together, these different scenarios help governments aim for the best, but plan for the worst. But they are only estimates, never certainties."
- by foxnews
- descember 09, 2016
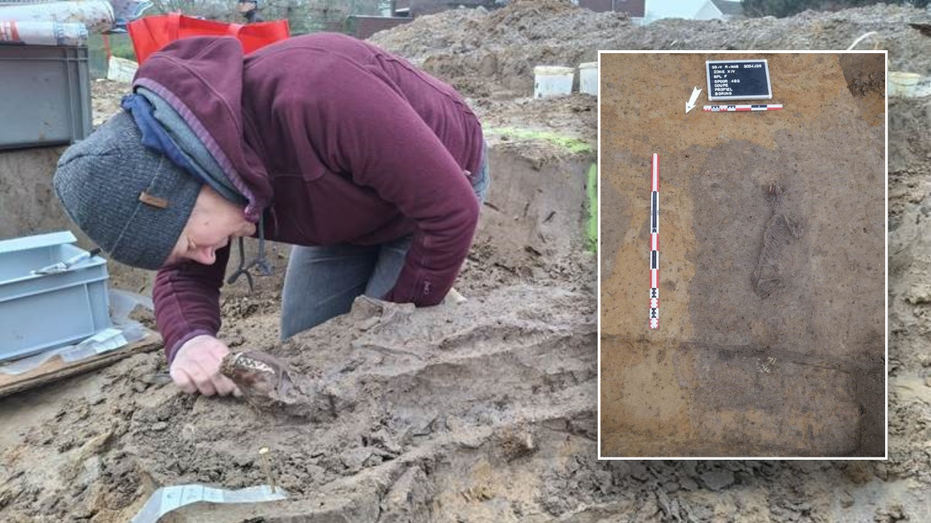
Ancient settlement reveals remains of 1,800-year-old dog, baffling experts: 'Preserved quite well'
Archaeologists have recently unearthed the remarkably well-preserved remains of a dog from ancient Rome, shedding light on the widespread practice of ritual sacrifice in antiquity.
read more


